Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Modulating Signals¶
Apply amplitude modulation to simulated signals.
Amplitude Modulation¶
Amplitude modulation is a where the amplitude of a signal is modulate by another signal.
# Import sim functions
from neurodsp.sim import sim_powerlaw, sim_oscillation
from neurodsp.utils import set_random_seed
# Import sim functions for modulation
from neurodsp.sim import sim_modulated_signal
from neurodsp.sim.utils import modulate_signal
# Import utilities for plotting data
from neurodsp.utils import create_times
from neurodsp.plts import plot_time_series
# Set the random seed, for consistency simulating data
set_random_seed(0)
# Set some general settings, to be used across all simulations
n_seconds = 10
fs = 1000
times = create_times(n_seconds, fs)
Modulate Signal¶
To apply amplitude modulation, we can use the modulate_signal() function.
Using this approach, creating a modulated signal includes the following steps:
Simulate a signal
Simulate a modulator
Apply the modulator to the signal
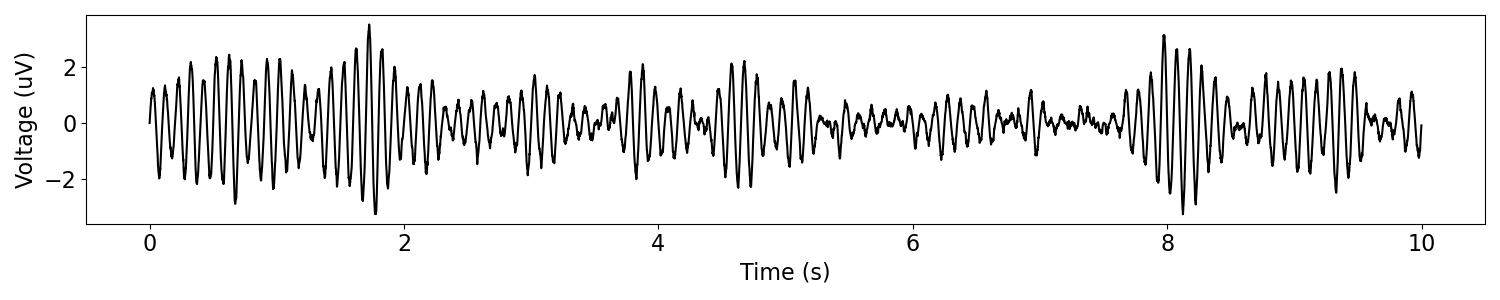
Oscillatory Amplitude Modulation¶
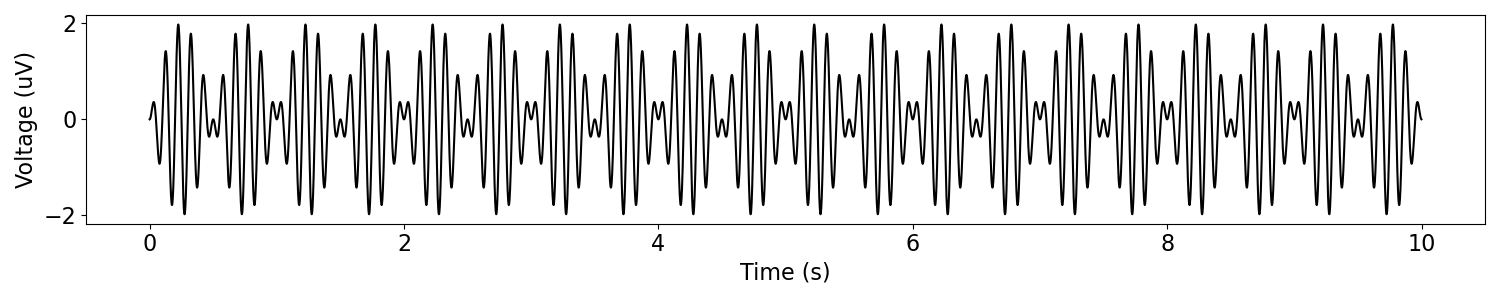
To start, we will simulate an an oscillatory signal that has oscillatory amplitude modulation.
# Simulate base signal, as a 10 Hz oscillation
sig = sim_oscillation(n_seconds, fs, 10)
# Simulate a modulating signal, here a 1 Hz sine wave
mod = sim_oscillation(n_seconds, fs, 1)
# Apply the amplitude modulation to the signal
msig = modulate_signal(sig, mod)
# Plot the amplitude modulated signal
plot_time_series(times, msig)
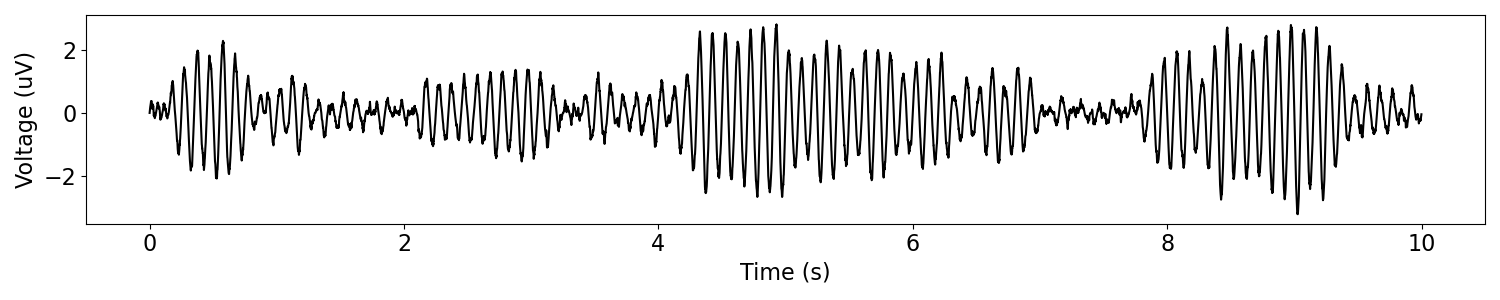
Aperiodic Amplitude Modulation¶
Next, we will apply a different amplitude modulation, this time applying aperiodic amplitude modulation to the same oscillatory signal.
# Simulate a different modulating signal, this time
mod = sim_powerlaw(n_seconds, fs, exponent=-2)
# Apply the amplitude modulation to the signal
msig = modulate_signal(sig, mod)
# Plot the amplitude modulated signal
plot_time_series(times, msig)
Call signatures¶
In the above, we explicitly simulated both the base signal and the modulating signal.
When using modulate_signal(), we can also pass in instruction
Note also that any signal can be the base and/or the modulator.
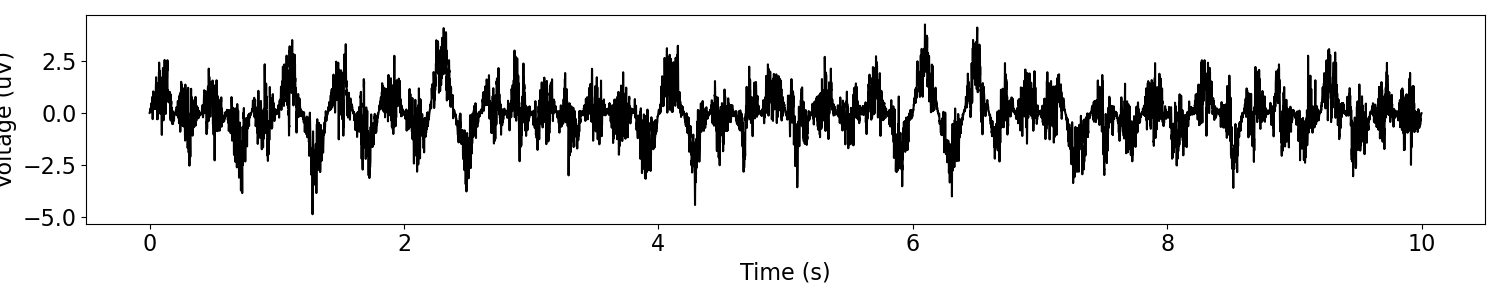
In the following example, we will amplitude modulate a powerlaw signal with an oscillatory modulation.
# Simulate a new signal to modulate, this time an aperiodic signal
sig = sim_powerlaw(n_seconds, fs, exponent=-1)
# Define and apply amplitude modulation to the signal
msig = modulate_signal(sig, 'sim_oscillation', fs, {'freq' : 2.5})
# Plot the amplitude modulated signal
plot_time_series(times, msig)
Sim modulated signal¶
If you want to simulated amplitude modulated signals directly,
there is also the sim_modulated_signal() function.
Instead of taking in pre-computed signals, this function takes in instructions for both the main and modulated signal, creates both and then returns the modulated signal.
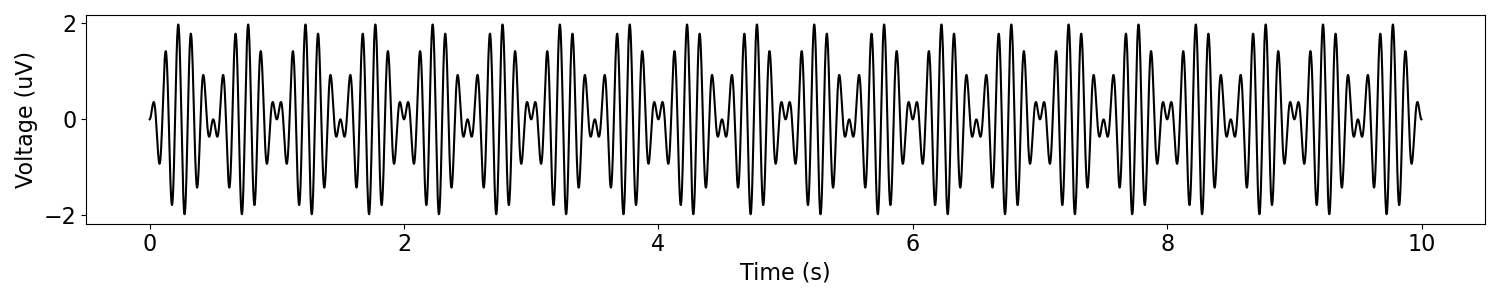
# Simulate a modulated signal, passing in instruction for the main and modulating signal
msig = sim_modulated_signal(n_seconds, fs,
'sim_oscillation', {'freq' : 10},
'sim_oscillation', {'freq' : 1})
# Plot the amplitude modulated signal
plot_time_series(times, msig)
# Simulate another modulated signal
msig = sim_modulated_signal(n_seconds, fs,
'sim_oscillation', {'freq' : 10},
'sim_powerlaw', {'exponent' : -2})
# Plot the amplitude modulated signal
plot_time_series(times, msig)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.401 seconds)