neurodsp.rhythm.compute_lagged_coherence¶
- neurodsp.rhythm.compute_lagged_coherence(sig, fs, freqs, n_cycles=3, return_spectrum=False)[source]¶
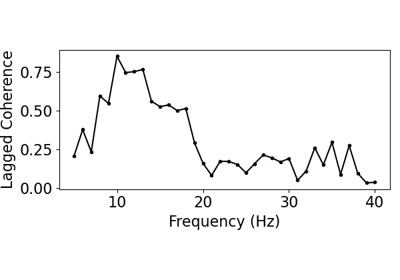
Compute lagged coherence, reflecting the rhythmicity across a frequency range.
- Parameters:
- sigarray
Time series.
- fsfloat
Sampling rate, in Hz.
- freqs1d array or list of float
The frequency values at which to estimate lagged coherence. If array, defines the frequency values to use. If list, define the frequency range, as [freq_start, freq_stop, freq_step]. The freq_step is optional, and defaults to 1. Range is inclusive of freq_stop value.
- n_cyclesfloat or list of float, default: 3
The number of cycles to use to compute lagged coherence, for each frequency. If a single value, the same number of cycles is used for each frequency. If a list or list_like, there should be a value corresponding to each frequency.
- return_spectrumbool, optional, default: False
If True, return the lagged coherence for all frequency values. Otherwise, only the mean lagged coherence value across the frequency range is returned.
- Returns:
- lcsfloat or array
If return_spectrum is False: mean lagged coherence value across the frequency range. If return_spectrum is True: lagged coherence values for all frequencies.
- freqs1d array
Frequencies, corresponding to the lagged coherence values, in Hz. Only returned if return_spectrum is True.
Notes
The lagged coherence algorithm is described in [1].
References
[1]Fransen, A. M., van Ede, F., & Maris, E. (2015). Identifying neuronal oscillations using rhythmicity. NeuroImage, 118, 256-267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.06.003
Examples
Compute lagged coherence for a simulated signal with beta oscillations:
>>> from neurodsp.sim import sim_combined >>> sim_components = {'sim_synaptic_current': {}, ... 'sim_bursty_oscillation': {'freq': 20, ... 'burst_params': {'enter_burst' : 0.50, ... 'leave_burst' : 0.25}}} >>> sig = sim_combined(n_seconds=10, fs=500, components=sim_components) >>> lag_cohs = compute_lagged_coherence(sig, fs=500, freqs=(5, 35))